Note
This tutorial was generated from an IPython notebook that can be downloaded here.
Create 2D region masks¶
In this tutorial we will show how to create 2D mask for arbitrary latitude and longitude grids.
Import regionmask and check the version:
import regionmask
regionmask.__version__
'0.5.0+dev'
Load xarray and the tutorial data:
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
Creating a mask¶
We define a lon/ lat grid with a 1° grid spacing, where the points define the center of the grid.
lon = np.arange(-179.5, 180)
lat = np.arange(-89.5, 90)
We create a mask with the SREX regions (Seneviratne et al., 2012).
regionmask.defined_regions.srex
<regionmask.Regions>
Name: SREX
Source: Seneviratne et al., 2012 (https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2...
Regions:
1 ALA Alaska/N.W. Canada
2 CGI Canada/Greenl./Icel.
3 WNA W. North America
4 CNA C. North America
5 ENA E. North America
.. ... ...
22 EAS E. Asia
23 SAS S. Asia
24 SEA S.E. Asia
25 NAU N. Australia
26 SAU S. Australia/New Zealand
[26 regions]
The function mask determines which gripoints lie within the polygon
making up the each region:
mask = regionmask.defined_regions.srex.mask(lon, lat)
mask
- lat: 180
- lon: 360
- nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan ... nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan
array([[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan], [nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan], [nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan], ..., [nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan], [nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan], [nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]]) - lat(lat)float64-89.5 -88.5 -87.5 ... 88.5 89.5
array([-89.5, -88.5, -87.5, -86.5, -85.5, -84.5, -83.5, -82.5, -81.5, -80.5, -79.5, -78.5, -77.5, -76.5, -75.5, -74.5, -73.5, -72.5, -71.5, -70.5, -69.5, -68.5, -67.5, -66.5, -65.5, -64.5, -63.5, -62.5, -61.5, -60.5, -59.5, -58.5, -57.5, -56.5, -55.5, -54.5, -53.5, -52.5, -51.5, -50.5, -49.5, -48.5, -47.5, -46.5, -45.5, -44.5, -43.5, -42.5, -41.5, -40.5, -39.5, -38.5, -37.5, -36.5, -35.5, -34.5, -33.5, -32.5, -31.5, -30.5, -29.5, -28.5, -27.5, -26.5, -25.5, -24.5, -23.5, -22.5, -21.5, -20.5, -19.5, -18.5, -17.5, -16.5, -15.5, -14.5, -13.5, -12.5, -11.5, -10.5, -9.5, -8.5, -7.5, -6.5, -5.5, -4.5, -3.5, -2.5, -1.5, -0.5, 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5, 8.5, 9.5, 10.5, 11.5, 12.5, 13.5, 14.5, 15.5, 16.5, 17.5, 18.5, 19.5, 20.5, 21.5, 22.5, 23.5, 24.5, 25.5, 26.5, 27.5, 28.5, 29.5, 30.5, 31.5, 32.5, 33.5, 34.5, 35.5, 36.5, 37.5, 38.5, 39.5, 40.5, 41.5, 42.5, 43.5, 44.5, 45.5, 46.5, 47.5, 48.5, 49.5, 50.5, 51.5, 52.5, 53.5, 54.5, 55.5, 56.5, 57.5, 58.5, 59.5, 60.5, 61.5, 62.5, 63.5, 64.5, 65.5, 66.5, 67.5, 68.5, 69.5, 70.5, 71.5, 72.5, 73.5, 74.5, 75.5, 76.5, 77.5, 78.5, 79.5, 80.5, 81.5, 82.5, 83.5, 84.5, 85.5, 86.5, 87.5, 88.5, 89.5]) - lon(lon)float64-179.5 -178.5 ... 178.5 179.5
array([-179.5, -178.5, -177.5, ..., 177.5, 178.5, 179.5])
mask is now a xarray.Dataset with shape lat x lon (if you
need a numpy array use mask.values). Gridpoints that do not fall in
a region are NaN, the gridpoints that fall in a region are encoded
with the number of the region (here 1 to 26).
We can now plot the mask:
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
f, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree()))
ax.coastlines()
mask.plot(ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), add_colorbar=False);
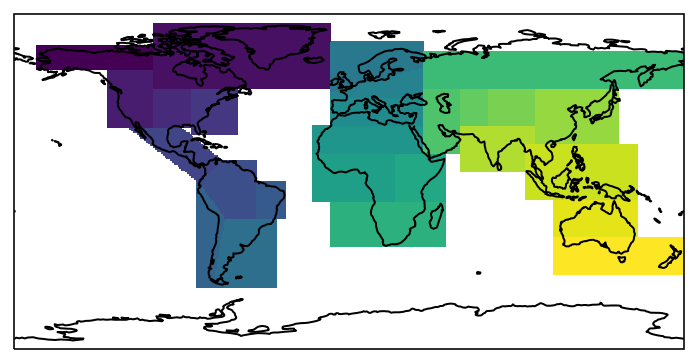
Working with a mask¶
masks can be used to select data in a certain region and to calculate regional averages - let’s illustrate this with a ‘real’ dataset:
airtemps = xr.tutorial.load_dataset("air_temperature")
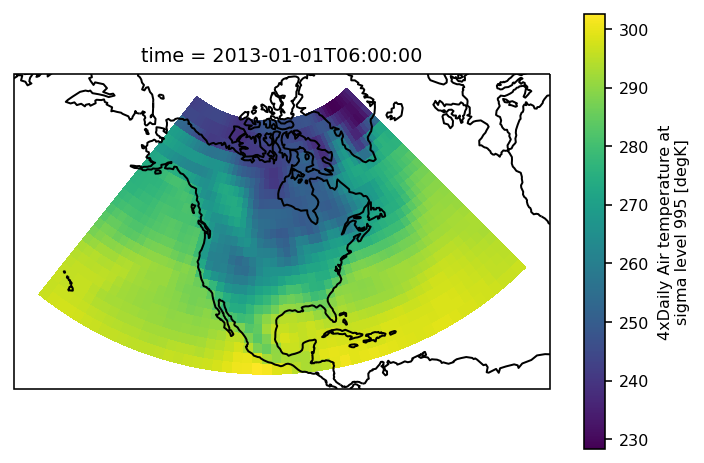
The example data is a temperature field over North America. Let’s plot the first time step:
# load plotting libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
# choose a good projection for regional maps
proj = ccrs.LambertConformal(central_longitude=-100)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
airtemps.isel(time=1).air.plot.pcolormesh(ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines();
Conviniently we can directly pass an xarray object to the mask
function. It gets the longitude and latitude from the DataArray/
Dataset and creates the mask. If the longitude and latitude in
the xarray object are not called "lon" and "lat", respectively;
you can pass their name via the lon_name and lat_name keyword.
mask = regionmask.defined_regions.srex.mask(airtemps)
Note
From version 0.5 regionmask automatically detects wether the longitude needs to be wrapped around, i.e. if the regions extend from -180° E to 180° W, while the grid goes from 0° to 360° W as in our example:
lon = airtemps.lon
print(
"Grid extent: {:3.0f}°E to {:3.0f}°E".format(lon.values.min(), lon.values.max())
)
bounds = regionmask.defined_regions.srex.bounds_global
print("Region extent: {:3.0f}°E to {:3.0f}°E".format(bounds[0], bounds[2]))
Grid extent: 200°E to 330°E
Region extent: -168°E to 180°E
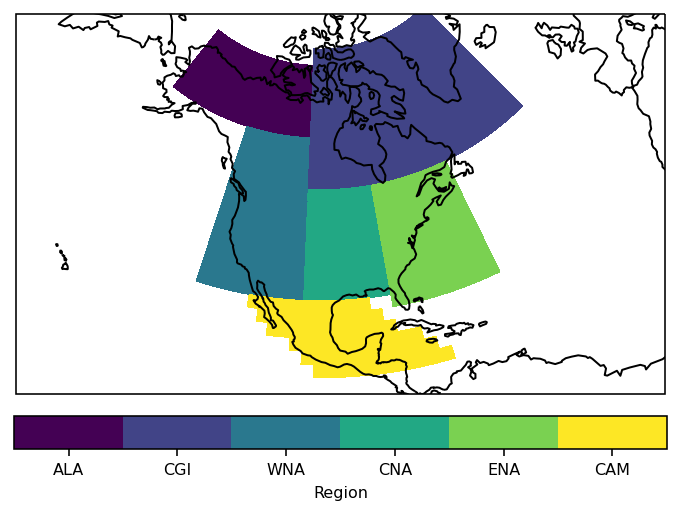
Let’s plot the mask of the regions:
proj = ccrs.LambertConformal(central_longitude=-100)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
low = mask.min()
high = mask.max()
levels = np.arange(low - 0.5, high + 1)
h = mask.plot.pcolormesh(
ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), levels=levels, add_colorbar=False
)
# for colorbar: find abbreviations of all regions that were selected
reg = np.unique(mask.values)
reg = reg[~np.isnan(reg)]
abbrevs = regionmask.defined_regions.srex[reg].abbrevs
cbar = plt.colorbar(h, orientation="horizontal", fraction=0.075, pad=0.05)
cbar.set_ticks(reg)
cbar.set_ticklabels(abbrevs)
cbar.set_label("Region")
ax.coastlines()
# fine tune the extent
ax.set_extent([200, 330, 10, 75], crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
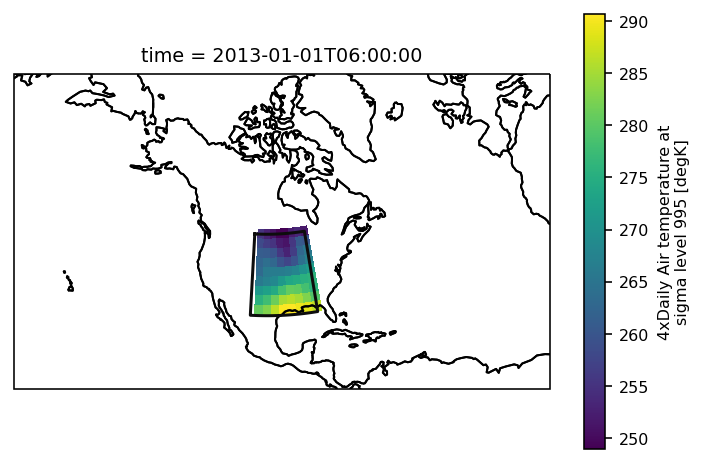
We want to select the region ‘Central North America’. Thus we first need to find out which number this is:
CNA_index = regionmask.defined_regions.srex.map_keys("C. North America")
CNA_index
4
Select using where¶
xarray provides the handy where function:
airtemps_CNA = airtemps.where(mask == CNA_index)
Check everything went well by repeating the first plot with the selected region:
# choose a good projection for regional maps
proj = ccrs.LambertConformal(central_longitude=-100)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
regionmask.defined_regions.srex[["CNA"]].plot(ax=ax, add_ocean=False, add_label=False)
airtemps_CNA.isel(time=1).air.plot.pcolormesh(ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines();
Looks good - let’s take the area average and plot the time series. From
version 0.15.1 xarray includes a function to calculate the weighted mean
- we use cos(lat) as proxy of the grid cell area
weights = np.cos(np.deg2rad(airtemps.lat))
ts_airtemps_CNA = airtemps_CNA.weighted(weights).mean(dim=("lat", "lon")) - 273.15
ts_airtemps = airtemps.weighted(weights).mean(dim=("lat", "lon")) - 273.15
# and the line plot
f, ax = plt.subplots()
ts_airtemps_CNA.air.plot.line(ax=ax, label="Central North America")
ts_airtemps.air.plot(ax=ax, label="Entire Domain")
ax.axhline(0, color="0.1", lw=0.5)
plt.legend(ncol=2);
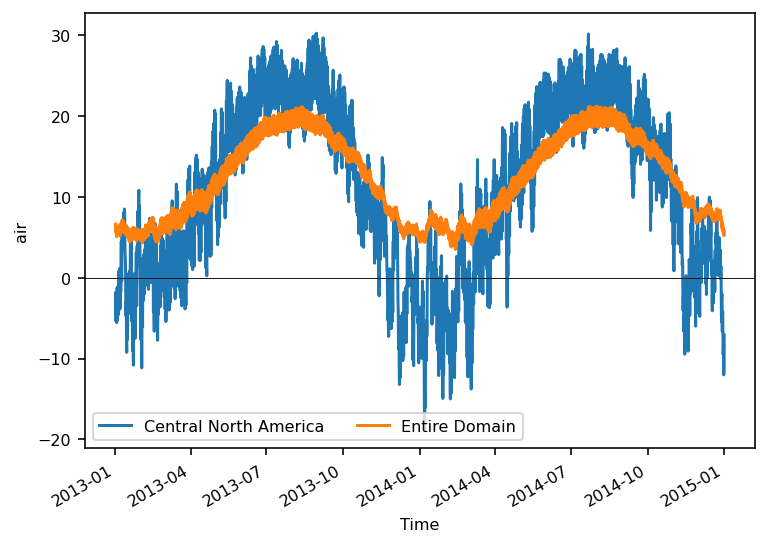
To get the regional average over each region you need to loop over them.
Select using groupby¶
Warning
Using groupby offers some convinience and is faster than using where and a loop. However, it cannot
currently be combinded with weighted (xarray GH3937).
Therefore I recommend using where.
# you can group over all integer values of the mask
airtemps_all = airtemps.groupby(mask).mean()
we can add the abbreviations and names of the regions to the DataArray
# extract the abbreviations and the names of the regions from regionmask
abbrevs = regionmask.defined_regions.srex[airtemps_all.region.values].abbrevs
names = regionmask.defined_regions.srex[airtemps_all.region.values].names
airtemps_all.coords["abbrevs"] = ("region", abbrevs)
airtemps_all.coords["names"] = ("region", names)
now we can select the regions in many ways
# as before, by the index of the region
r1 = airtemps_all.sel(region=CNA_index).air
# with the abbreviation
r2 = airtemps_all.isel(region=(airtemps_all.abbrevs == "WNA")).air.squeeze()
# with the long name
r3 = airtemps_all.isel(region=(airtemps_all.names == "E. North America")).air.squeeze()
regs = [r1, r2, r3]
Now, let’s plot the three selected regions:
f, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1, sharex=True)
for i, reg in enumerate(regs):
ax = axes[i]
reg.plot(ax=ax)
ax.set_title(reg.names.values)
plt.setp(axes, xlabel="")
f.tight_layout()
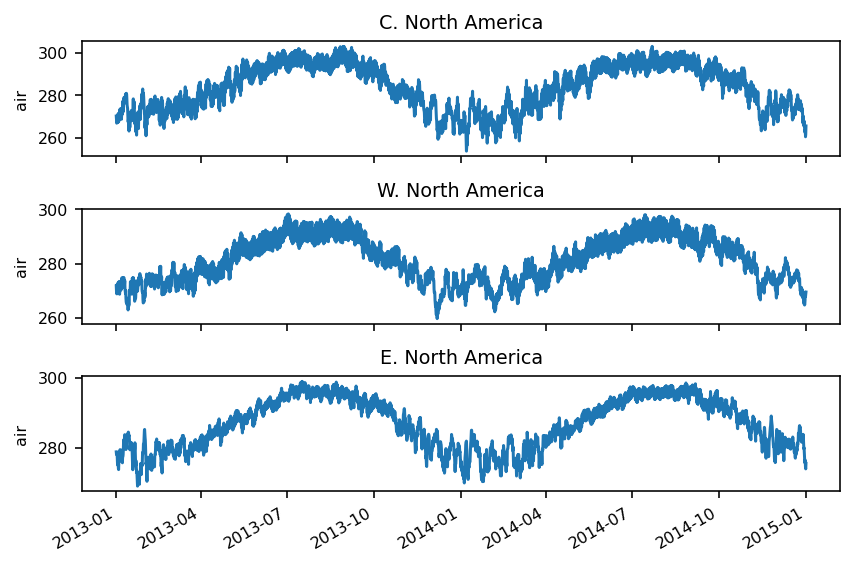
Multidimensional coordinates¶
Regionmask can also handle mutltidimensional longitude/ latitude grids (e.g. from a regional climate model). As xarray provides such an example dataset, we will use it to illustrate it. See also in the xarray documentation.
Load the tutorial data:
rasm = xr.tutorial.load_dataset("rasm")
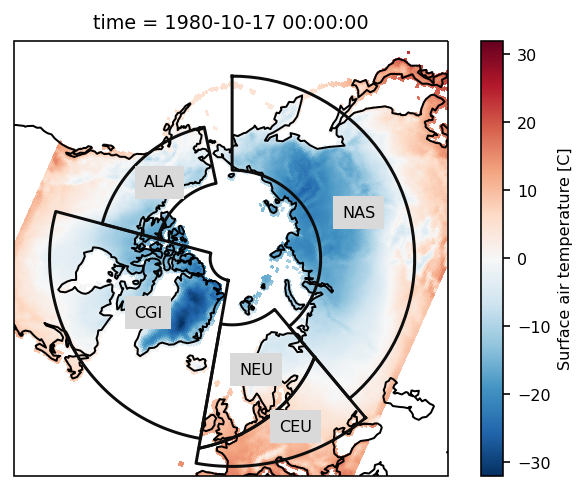
The example data is a temperature field over the Northern Hemisphere. Let’s plot the first time step:
# load plotting libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
# choose a projection
proj = ccrs.NorthPolarStereo()
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
ax.set_global()
rasm.isel(time=1).Tair.plot.pcolormesh(
ax=ax, x="xc", y="yc", transform=ccrs.PlateCarree()
)
# add the abbreviation of the regions
regionmask.defined_regions.srex.plot(
ax=ax, regions=[1, 2, 11, 12, 18], add_ocean=False, coastlines=False, label="abbrev"
)
ax.set_extent([-180, 180, 43, 90], ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines();
Again we pass the xarray object to regionmask. We have to specify
"xc" and "yc" as the longitude and latitude coordinates of the
array:
mask = regionmask.defined_regions.srex.mask(rasm, lon_name="xc", lat_name="yc")
mask
- y: 205
- x: 275
- nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan ... 14.0 14.0 14.0 14.0 14.0 14.0 14.0
array([[nan, nan, nan, ..., 5., 5., 5.], [nan, nan, nan, ..., 5., 5., 5.], [nan, nan, nan, ..., 5., 5., 5.], ..., [24., 24., 24., ..., 14., 14., 14.], [24., 24., 24., ..., 14., 14., 14.], [24., 24., 24., ..., 14., 14., 14.]]) - y(y)int640 1 2 3 4 5 ... 200 201 202 203 204
array([ 0, 1, 2, ..., 202, 203, 204])
- x(x)int640 1 2 3 4 5 ... 270 271 272 273 274
array([ 0, 1, 2, ..., 272, 273, 274])
- yc(y, x)float6416.53 16.78 17.02 ... 27.76 27.51
array([[16.53498637, 16.7784556 , 17.02222429, ..., 27.36301592, 27.11811045, 26.87289026], [16.69397341, 16.93865381, 17.18364512, ..., 27.5847719 , 27.33821848, 27.0913656 ], [16.85219179, 17.09808909, 17.34430872, ..., 27.80584314, 27.55764558, 27.30915621], ..., [17.31179033, 17.56124674, 17.81104646, ..., 28.4502485 , 28.19718339, 27.94384744], [17.15589701, 17.40414034, 17.65272318, ..., 28.23129632, 27.97989251, 27.72821596], [16.99919497, 17.24622904, 17.49358736, ..., 28.01160028, 27.76185586, 27.51182726]]) - xc(y, x)float64189.2 189.4 189.6 ... 17.15 16.91
array([[189.22293223, 189.38990916, 189.55836619, ..., 293.77906088, 294.0279241 , 294.27439931], [188.96836986, 189.13470591, 189.30253733, ..., 294.05584005, 294.30444387, 294.55065969], [188.71234264, 188.87800731, 189.04515208, ..., 294.335053 , 294.58337453, 294.8292928 ], ..., [124.04724025, 123.88362026, 123.71852016, ..., 16.83171831, 16.58436953, 16.33949649], [123.78686428, 123.62254238, 123.45672512, ..., 17.11814486, 16.87043749, 16.62518298], [123.52798366, 123.36295986, 123.1964407 , ..., 17.40209947, 17.1540526 , 16.90845095]])
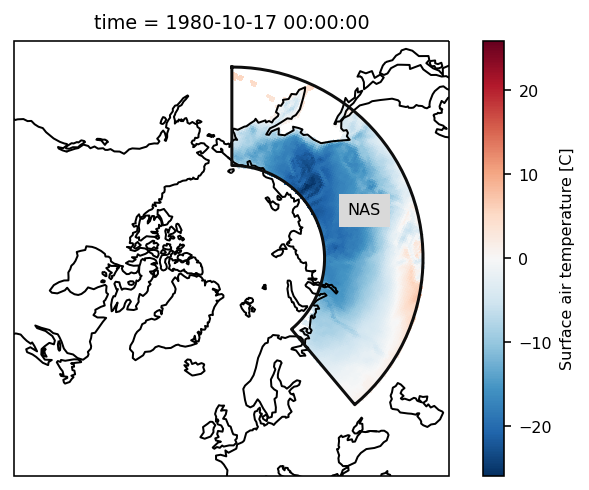
We want to select the region ‘NAS’ (Northern Asia).
Select using where¶
We have to select by index (the number of the region), we thus map from the abbreviation to the index.
rasm_NAS = rasm.where(mask == regionmask.defined_regions.srex.map_keys("NAS"))
Check everything went well by repeating the first plot with the selected region:
# choose a projection
proj = ccrs.NorthPolarStereo()
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
ax.set_global()
rasm_NAS.isel(time=1).Tair.plot.pcolormesh(
ax=ax, x="xc", y="yc", transform=ccrs.PlateCarree()
)
# add the abbreviation of the regions
regionmask.defined_regions.srex.plot(
ax=ax, regions=["NAS"], add_ocean=False, coastlines=False, label="abbrev"
)
ax.set_extent([-180, 180, 45, 90], ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines();
References¶
Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation (SREX, Seneviratne et al., 2012: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/SREX-Ch3-Supplement_FINAL-1.pdf)