Note
This tutorial was generated from an IPython notebook that can be downloaded here.
Working with geopandas (shapefiles)¶
regionmask includes support for regions defined as geopandas
GeoDataFrames. These are often shapefiles, which can be opened in
the formats .zip or .shp with
geopandas.read_file(url_or_path).
There are two possibilities:
mask_geopandas(andmask_3D_geopandas): directly create a mask from a geopandas GeoDataFrame (or GeoSeries)to_geopandas: convert a GeoDataFrame to aRegionsobject (regionmask’s internal data container), which can then be used to mask, plot and select regions.
As always, start with the imports:
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import geopandas as gp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import regionmask
regionmask.__version__
'0.5.0+dev'
Opening an example shapefile¶
The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) offers a shapefile containing the outlines of continens [1].
continents = gp.read_file(
"https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2006/1187/basemaps/continents/continents.zip"
)
display(continents)
CONTINENT geometry
0 Asia MULTIPOLYGON (((93.27554 80.26361, 93.31304 80...
1 North America MULTIPOLYGON (((-25.28167 71.39166, -25.32889 ...
2 Europe MULTIPOLYGON (((58.06138 81.68776, 57.98055 81...
3 Africa MULTIPOLYGON (((0.69465 5.77337, 0.66667 5.803...
4 South America MULTIPOLYGON (((-81.71306 12.49028, -81.72014 ...
5 Oceania MULTIPOLYGON (((-177.39334 28.18416, -177.3958...
6 Australia MULTIPOLYGON (((142.27997 -10.26556, 142.21053...
7 Antarctica MULTIPOLYGON (((51.80305 -46.45667, 51.72139 -...
1. mask_geopandas and mask_3D_geopandas¶
mask_geopandas allows to directly create a mask from a geodataframe:
lon = np.arange(-180, 180)
lat = np.arange(-90, 90)
mask = regionmask.mask_geopandas(continents, lon, lat)
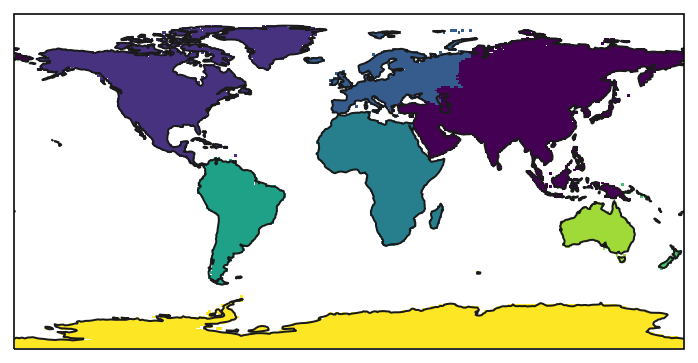
Let’s plot the new mask:
f, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree()))
mask.plot(
ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), add_colorbar=False,
)
ax.coastlines(color="0.1");
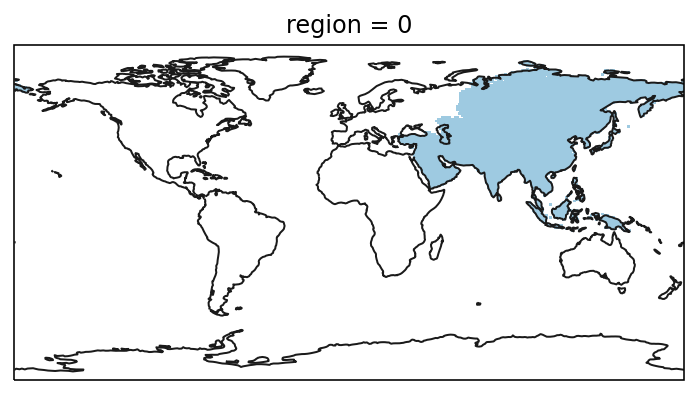
Similarly a 3D boolean mask can be created from a geodataframe:
from matplotlib import colors as mplc
cmap1 = mplc.ListedColormap(["none", "#9ecae1"])
mask_3D = regionmask.mask_3D_geopandas(continents, lon, lat)
f, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree()))
mask_3D.sel(region=0).plot(
ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), add_colorbar=False, cmap=cmap1,
)
ax.coastlines(color="0.1");
2. to_geopandas¶
Creating a Regions object with regionmask.from_geopandas only
requires a GeoDataFrame:
continents_regions = regionmask.from_geopandas(continents)
display(continents_regions)
<regionmask.Regions>
Name: unnamed
Regions:
0 r0 Region0
1 r1 Region1
2 r2 Region2
3 r3 Region3
4 r4 Region4
5 r5 Region5
6 r6 Region6
7 r7 Region7
[8 regions]
This creates default names ("Region0", …, "RegionN") and
abbreviations ("r0", …, "rN").
However, it is often advantageous to use columns of the GeoDataFrame as
names and abbrevs. If no column with abbreviations is available, you can
use abbrevs='_from_name', which creates unique abbreviations using
the names column.
continents_regions = regionmask.from_geopandas(
continents, names="CONTINENT", abbrevs="_from_name", name="continent"
)
display(continents_regions)
<regionmask.Regions>
Name: continent
Regions:
0 Asi Asia
1 NorAme North America
2 Eur Europe
3 Afr Africa
4 SouAme South America
5 Oce Oceania
6 Aus Australia
7 Ant Antarctica
[8 regions]
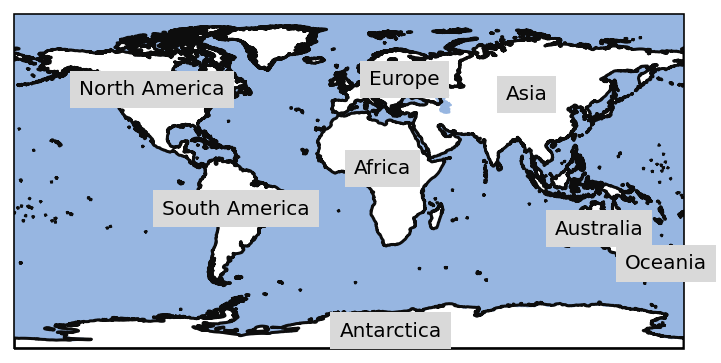
As usual the newly created Regions object can be plotted on a world
map:
continents_regions.plot(label="name", coastlines=False);
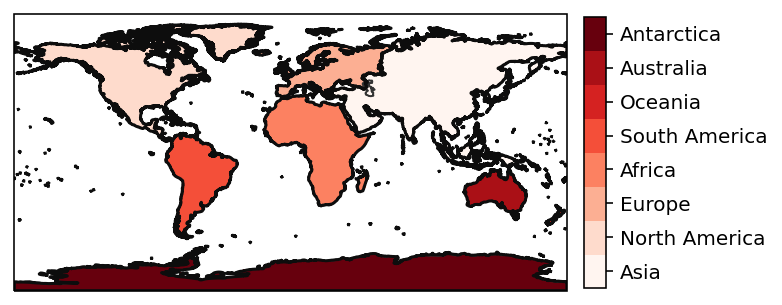
And to create mask a mask for arbitrary latitude/ longitude grids:
lon = np.arange(0, 360)
lat = np.arange(-90, 90)
mask = continents_regions.mask(lon, lat)
which can then be plotted
f, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree()))
h = mask.plot(
ax=ax,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
cmap="Reds",
add_colorbar=False,
levels=np.arange(-0.5, 8),
)
cbar = plt.colorbar(h, shrink=0.625, pad=0.025, aspect=12)
cbar.set_ticks(np.arange(8))
cbar.set_ticklabels(continents_regions.names)
ax.coastlines(color="0.2")
continents_regions.plot_regions(add_label=False);
References¶
[1] Environmental Systems Research , Inc. (ESRI), 20020401, World Continents: ESRI Data & Maps 2002, Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc. (ESRI), Redlands, California, USA.